Hydraulic Fittings Size Chart
Hydraulic hose fittings are very useful when it becomes necessary to connect various conductors such as tubes, pipes, and hoses in a hydraulic system. Most of these connections will have a male and female component to accommodate the connection and will assist with the process of containing and directing the flow of fluid; while also preventing any leakages and maintaining pressure in the lines. Various types of fitting allow the designer to change the flow of the fluid, to split the flow of the fluid, or to elevate the lines. Below we’ve compiled a hydraulic fittings size chart describing some of the more common fitting sizes and types currently in use by pipe fitters and other professionals.
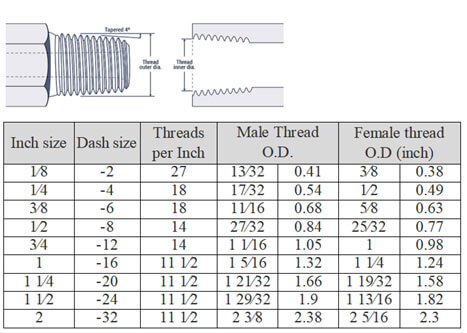
National Pipe Tapered Fuel (NPTF)
NPTF fittings feature both male and female threads that form a tight, “dry seal” due to thread deformation. For an even tighter seal, Teflon tape or pipe dope can be used. Although the NFPA advises against using NPTF for hydraulic systems, they are still common in fluid piping setups. Note: NPTF and BSPT connectors may look similar but are not interchangeable.
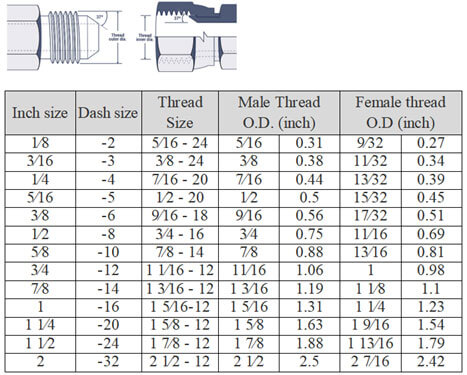
National Pipe straight mechanical (NPSM)
NPSM connectors have straight threads with the male end featuring a 30° internal chamfer and the female end an inverted 30° seat. This design forms a leak-proof mechanical connection, making NPSM connectors popular in fluid power systems. Notably, a female NPSM can effectively seal with a chamfered male NPTF.
JIC 37° Flare (SAE J514)
JIC fittings, commonly used in hydraulic systems, have 37° flare connectors with both male and female parts featuring a 37° flare seat and straight threads. When connected, the flare seats form a seal, while the straight threads provide a mechanical bond.
It’s important to highlight: Even though many SAE J514 threads may resemble SAE 45° flare threads, their seating angles are different.
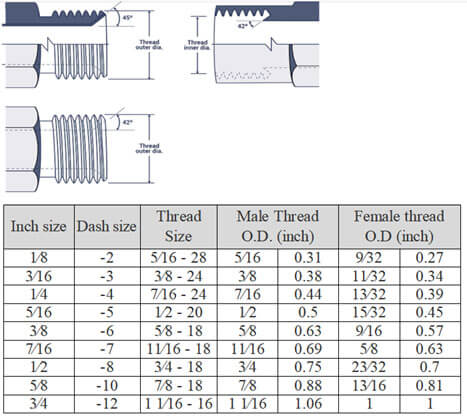
SAE 45° Flare (SAE J512)
SAE 45° flare connectors are commonly used in low-pressure applications like refrigerant, fuel lines, and automotive piping. Both parts feature a 45° flare seat, creating a strong mechanical bond when connected, with the seal forming at the flare seat.
Keep in mind: While SAE 45° flare connectors may resemble JIC 37° flare connectors, they differ in seating angles.
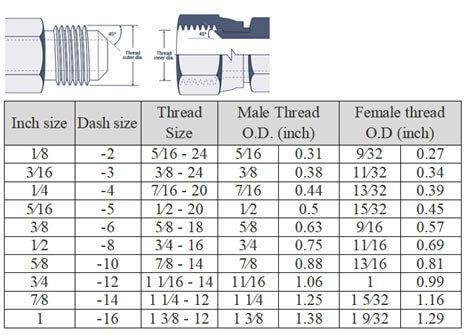
SAE Straight Thread O-ring (O-Ring Boss)-
SAE J1926-1 and ISO 11296-1
ORB fittings feature a female port with a sealing face, chamfer, and straight threads, while the male connector includes an O-ring and straight threads. The connection is sealed when the O-ring fits snugly into the chamfer, and the interlocking threads ensure a robust mechanical bond. This type of connection is frequently used in high-pressure hydraulic systems.
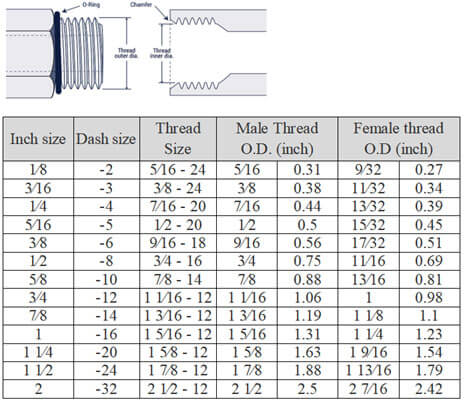
Flareless Compression (SAE J514)

O-Ring Face Seal (SAE J1453)
ORFS fittings offer excellent leak protection and are suitable for applications up to 6000 psi. The male part features an O-ring and straight threads, while the female part has a flat machined surface and straight threads. The seal is formed when the male’s O-ring presses against the female’s flat surface, secured by the swivel nut on the female side.

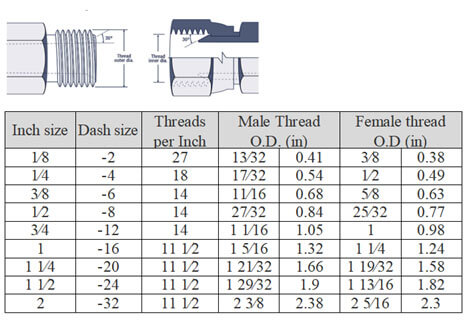
SAE Inverted Flare (SAE J512)
SAE inverted flare fittings are common in automotive systems. The male connector has a 42° seat and a 45° flared male tubing, while the female part offers a 42° seat as the sealing surface. When connected, their threads interlock, ensuring a sturdy mechanical bond.